Rate of Reaction Calculation
A chemical reactions rate law is an equation that describes the relationship between the concentrations of reactants in the reaction and the reaction rate. Equation of Rate of a Chemical Reaction Rate of disappearance of R Decrease in concentration of Rtime taken -Δ RΔt and rate of appearance of P Increase in concentration of Ptime.

How Do I Determine Rate Of Reaction Or Kinetics Of Reaction Without Taking Into Consideration The Reactant Concentration
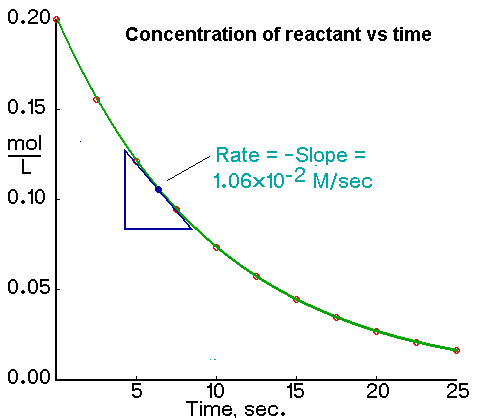
Determining the Initial Rate from a Plot of Concentration Versus Time The initial rate of a reaction is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction ie when t 0.

. However this value is not technically a constant because it includes the. The reaction rate is the change in the concentration of either the reactant or the product over a period of. Rate of reaction of C ΔC Δt The overall rate of reaction should be the same whichever component we measure.
The rate of reaction is shown to be dependent on the concentration terms of reactant A and reactant B. This equation is sometimes written as. The rate of the reaction is.
Calculating Rate of Reaction in a Snap. Q10 is a unitless quantity. If the rate of the reaction is completely temperature.
It is the factor by which the rate increases when the temperature is raised by ten degrees. No matter which quantity is measured during the course of a reaction the average rate of reaction can be calculated using the equation below. The rate of reaction can be analysed by plotting a graph of mass or volume of product formed against time.
It is noted that the. R k T A n B n k T is the rate constant or reaction rate coefficient. As mentioned earlier the rate of reaction can be calculated a couple of different ways.
Each point in the graph corresponds to one beaker in Figure 142. Photosynthesis Calculation worksheet OCR Biology Homework. We can measure the quantity of reactant used up or quantity of product formed in a reaction.
This is the second factor that we need to know in order to calculate the rate of a reaction. Rate of chemical reaction Change in concentrationTime Interval r ΔCΔt This formula uses 3 Variables Variables Used Rate of chemical reaction - Measured in Mole per Meter³ Second -. Unlock the full GCSE Chemistry course at httpbitly35RsKBa created by Marianne Chemistry expert at SnapReviseSn.
Σ by the total volume of the core V gives us the total number of reactions occurring in the. The graph shows this for two reactions. The steeper the line the greater the rate.
First the general rate of reaction formula that involves the rate constant for a general. The rate constant of the reaction CFsub 3 Osub 2 yields CFsub 3O O in the range of 700-2000 K has been calculated in the framework of the transition state method. Finding rates of reaction in photosynthesis Specification references 521 M31 M32 M35 M41 Learning outcomes.
The rate of a chemical reaction is calculated in terms of a decrease in the concentration of any of the reactants per unit time or an increase in the concentration of any of. To determine the average rate of reaction the two time intervals t 1 and t 2 are marked on the time axis ie x-axis and. The initial rate is equal to.
Calculation of Average Rate of Reaction. Then Rate of reaction A α B β. Multiplying the reaction rate per unit volume RR Ф.
01 g of calcium carbonate is added to excess. So we divide the rate of each component by its coefficient. Reaction Rate and Reactor Power Calculation.
In the standard form the rate. Examples about the calculation of the average rate of reaction and instantaneous rate of reaction are shown below. Or Rate K A α B β.
This expression is termed.

Chemical Equilibrium Reaction Online College Chemistry Courses College Chemistry Online Degree Chemical Kinetics

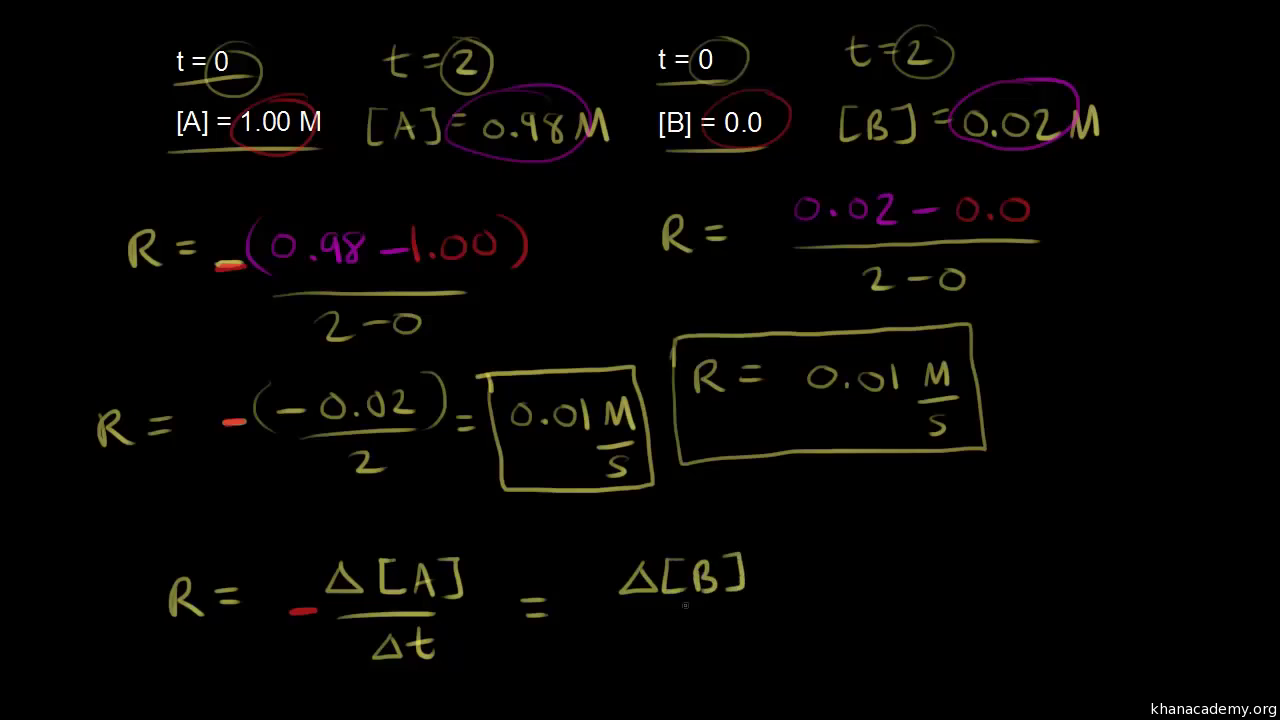
No comments for "Rate of Reaction Calculation"
Post a Comment